Complete Guide to How Many Calories You Should Eat to Gain Muscle in 2025
“`html
How Many Calories You Should Eat to Gain Muscle in 2025
Understanding Caloric Needs for Muscle Gain
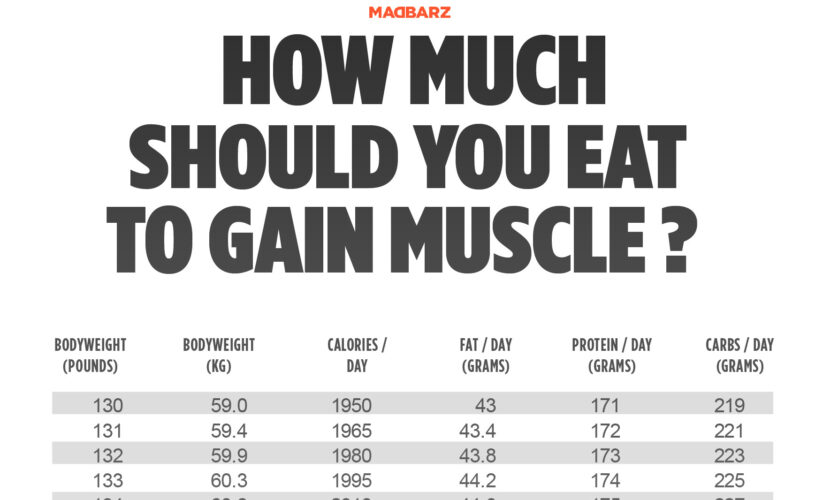
To effectively gain muscle, it’s crucial to understand how to calculate your caloric needs. When considering **how many calories to gain muscle**, you’ll want to assess your current weight, activity level, and fitness goals. Increasing your calorie intake is essential for creating a **calorie surplus for muscle growth**. By consuming more calories than your body burns, you provide it with the necessary energy to build new muscle tissues. For many people, achieving a balance between daily caloric needs for muscle gain and macronutrient distribution is key to an effective **muscle-building diet**.
Why Caloric Surplus is Important
A **caloric surplus** is fundamental for muscle development. When you consume more calories than your body requires, it uses those extra calories to fuel workouts and repair muscles. This is where **recommended calories for muscle** come into play. Generally, you may need to consume an additional 250 to 500 calories above your maintenance level daily. This surplus allows your body to engage in **muscle hypertrophy**, a crucial phase in muscle gain. For instance, athletes focusing on gaining muscle should integrate a strategic **diet for muscle development** that concentrates on high-calorie yet nutritious foods.
Calculating Your Optimal Caloric Intake
To **calculate calories for muscle**, start by determining your Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR), the number of calories your body needs at rest. Several online tools and calculators can assist with this. Once you have your BMR, factor in your activity level to find your Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE). From there, you can adjust for a **calorie surplus for muscle growth**. Consider using a **muscle gain calorie calculator** for a more tailored approach that matches specific fitness routines.
Essential Nutrients for Muscle Growth
While calorie intake is vital, the type of calories matters just as much. Emphasizing **high protein foods for muscle** is crucial. Proteins serve as the building blocks for muscle tissues, so focusing on adequate protein sources can enhance recovery and support muscle synthesis significantly. Alongside protein, don’t neglect healthy fats and carbohydrates—key players in overall energy levels for workouts and metabolic processes.
Macronutrients Breakdown
A successful **muscle gain diet** typically consists of a balanced macronutrient ratio: approximately 40-60% carbohydrates, 25-35% protein, and 15-25% fats is a great starting point. **Nutrition for muscle growth** isn’t just about protein; carbohydrates fuel energy for workouts, and healthy fats support hormone production necessary for muscle growth and recovery. Including foods such as avocados, nuts, lean meats, and whole grains will help maximize caloric intake efficiency.
Snacking for Muscle Gain
For those looking to up their caloric consumption easily, snacking effectively between meals can be beneficial. Incorporate clever **high calorie snacks for bulking** that are rich in protein and healthy fats. Peanut butter, protein bars, and smoothies can also serve as excellent **snacks for muscle gain**. Always be mindful of your overall **protein intake for athletes**, targeting around 1.6 to 2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight, according to most guidelines.
The Role of Meal Timing and Frequency
Another high-impact strategy for muscle gain involves **meal frequency for muscle**. Eating several small meals throughout the day can help keep your metabolism active and your energy levels sustained. This method ensures you consistently consume the necessary calories needed for bulking. Splitting your total daily caloric needs into 5 to 6 meals can ease digestion and improve nutrient absorption.
Pre and Post Workout Nutrition
Focusing on nutrient timing is essential for enhancing muscle growth. Consuming a combination of protein and carbohydrates before workouts can significantly improve performance. Post-workout meals should quickly prioritize protein intake for muscle recovery. A balanced approach to **workout nutrition** leads to better muscle retention and growth. For example, a detailed **muscle gaining meal plan** would consist of a protein source paired with a healthy carb base like brown rice or quinoa after exercising.
Hydration and Muscle Recovery
Nutrient timing doesn’t end with food; hydration is a critical component, too. Staying adequately hydrated supports overall performance and prevents fatigue. Dehydration can hinder muscle recovery and affect workout performance. Water or electrolyte-rich beverages like coconut water should be part of any solid nutrition plan to maintain **hydration for muscle gain**. In summary, prioritize keeping yourself hydrated both during your workouts and in your daily routine.
Implementing and Adjusting Your Diet Plans
To achieve your muscle gaining goals, implementing effective adjustments to your diet is essential. Consistency matters more than perfection, focusing on your body’s **energy balance** and adjusting your calorie intake based on your results is necessary. Check in every few weeks to assess progress, adjusting accordingly to maintain an optimal pathway toward muscle development.
Staying Committed to Your Goals
Maintaining a **weight gain diet plan** can be daunting but rewarding. Document your meals and monitor any changes in body composition using calorie tracking applications. You might need to tweak your intake based on progress and activities. Develop a habit of planning meals to avoid last-minute decisions that could disrupt caloric goals. Meal prep for muscle gain can be a game changer, allowing for easy and quick access to nutritious options throughout the week.
Seeking Professional Guidance
If you find it challenging to determine an ideal calorie intake, consider consulting a nutritionist. Professional guidance can help create a personalized nutrition plan tailored to your needs, making sure that all aspects, including a **nutrition strategy for muscle gain**, align with your fitness goals. A professional can aid in pinpointing areas that might need adjustment and introduce strategies to maximize your results.
Key Takeaways
- Calculating calories for muscle gain involves determining your TDEE and ensuring a caloric surplus.
- Focus not only on calories but also the quality of those calories—prioritize protein and nutrient-rich foods.
- Meal frequency and nutrient timing play pivotal roles in muscle recovery and growth.
- Stay hydrated and consider both macro and micronutrient intake as critical components for muscle development.
- Monitoring progress and remaining flexible with your diet strategy can ensure ongoing improvements.
FAQ
1. What is the best way to calculate my calorie needs for muscle gain?
The most accurate method includes calculating your Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) and then adjusting it with your activity level to find your Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE). From there, add an additional 250-500 calories for muscle gain.
2. Can I still gain muscle while following a vegetarian or vegan diet?
Absolutely! High protein foods rich in plant-based sources, such as lentils, quinoa, and soy, can help you achieve the necessary protein intake. Ensure you incorporate diverse nutrient sources to meet your overall caloric needs.
3. How often should I eat when trying to gain muscle?
It’s generally recommended to eat every 3 to 4 hours to maintain energy levels and provide your muscles with constant nutrition to support growth. Aim for 5 to 6 meals/snacks daily.
4. How critical is the timing of my post-workout meal?
The timing can highly influence recovery. Consuming a balanced meal with protein and carbs within 30 minutes to two hours post-workout helps optimize recovery and replenishes muscle glycogen stores.
5. Are supplements necessary for muscle gain?
While whole foods should make up the majority of your diet, supplements like whey protein can help reach your protein goals conveniently; however, they are not strictly necessary if you can meet your caloric and protein needs through diet.
“`