Essential Guide to How to Find the Area of a Hexagon: Effective Methods for 2025
“`html
Essential Guide to How to Find the Area of a Hexagon
Understanding Hexagons and Their Geometry
A **hexagon** is a fascinating geometric shape characterized by its six sides and angles. Hexagons can be classified into two main categories: **regular hexagons**, which have equal side lengths and angles, and **irregular hexagons**, which do not. Understanding the geometry of hexagons is essential for applications in various fields such as architecture, engineering, and design. The **hexagon area formula** is crucial in calculating the area of these shapes, incorporating measurements like side lengths and the apothem, which helps customers and engineers in area determination of hexagons. This article dives deeper into techniques for finding the area of a hexagon, emphasizing the practical applications and mathematical significance of hexagonal shapes.
Regular vs Irregular Hexagons
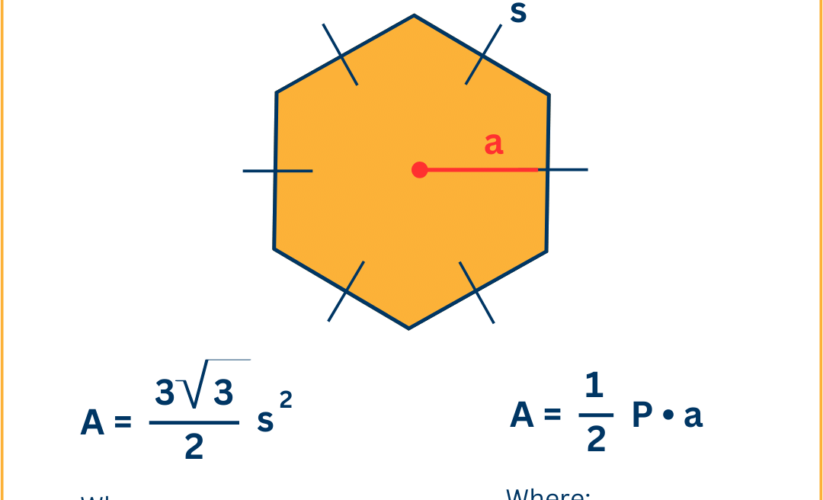
Regular hexagons feature equal side lengths and angles, giving them symmetry that facilitates easy area calculation. The formula used for calculating the area of a regular hexagon is:
Area = (3√3/2) × s²
where “s” represents the side length. In contrast, **irregular hexagons** do not adhere to these uniform measurements, which makes their area calculation more complex. Methods such as triangulation or dividing the shape into simpler polygons can be used for finding the area of irregular hexagons. By assessing both types, we can appreciate the diverse **geometric properties of hexagons** and their respective area formulas.
Hexagon Area Formula and Calculation Techniques
The **hexagon area formula** provides a foundation when calculating the area of hexagons. For a regular hexagon, the easy access to the length of a side enables simple computations. Alternatively, for irregular hexagons, one may need to rely on the diagonal method for **calculating polygon areas**. This could involve breaking down the hexagon into triangles and summing their areas—a practical method that provides thorough accuracy in **hexagonal area calculations**. Additionally, learning the derivation of hexagon area formulas reinforces the understanding of its properties in different applications.
Hexagon Area Using Apothem
The apothem is defined as the line segment from the center of a regular hexagon perpendicular to its sides. It serves a significant role in the **calculation of hexagon area**, particularly in more intricate designs where side lengths may not be immediately visible. The formula using the apothem is:
Area = (Perimeter × Apothem) / 2
In this scenario, the perimeter can be easily calculated from the side length. Thus, understanding the apothem’s use is crucial for accurate hexagon area visualization and measurement across various applications.
How to Calculate the Area Using the Apothem
To effectively use the apothem in area calculation, one must first discern the side length of the hexagon. Once the side length is found, calculating the perimeter is straightforward as:
Perimeter = 6 × s
Afterward, using the known average of the apothem allows for efficient area calculation through the formula provided. This method is particularly advantageous in **hexagonal tiling**, where precision in area is relevant to aesthetic and structural angles. Accurate application of this method can lead to enhanced design and construction methodologies.
Real-Life Applications of Hexagons
Hexagons frequently appear in nature and culture, as seen in patterns and tessellations. The **importance of hexagon area** surfaces in fields like architecture, where the calculated area influences designs and functionality. Their unique geometric formations allow for efficient designs in bee hives, tiling patterns, and a variety of engineering applications. Exploring how **hexagonal shapes** are utilized showcases the interdisciplinary nature of these shapes and their properties in practical scenarios, solidifying their relevance across different domains.
Hexagon Area Examples
Utilizing hexagon shapes in geometric exercises provides students and professionals alike with diverse applications of the area formulas. For example, one may calculate the area of a **regular hexagon** with a side length of 5 cm:
Area = (3√3/2) × (5 cm)² = 64,95 cm²
This practical example serves to enlighten users on how to implement hexagon area formulas in real-life conditions. Learning through practical exercises not only demystifies **calculating polygon areas** but also instills a sense of confidence in approaching complex shapes.
Exploring Hexagon Measurements in Nature
Observing **hexagon examples in nature**, such as honeycomb structures, provides a rich source of inspiration for understanding ecological efficiency. Investigating the area of a honeycomb hexagon involves similar calculations as one would with artificial designs. Such insights highlight the natural propensity toward hexagonal shapes, modeling structures both efficiently and aesthetically. Hexagons in nature can teach valuable lessons regarding mathematics’ relevance to biological and ecological systems.
Comparing Area Calculations: Regular vs Irregular Hexagons
A comparative analysis between **regular and irregular hexagons** sheds light on effective **area measurement methods**. Regular hexagons lend themselves to faster, more straightforward calculations, while irregular hexagons require a segmented approach—illustrating the differing complexity in calculating geometry shapes. By understanding these comparisons, analysts can derive best practices for interpreting and measuring area in various contexts, ensuring accuracy and consistency across applications.
Key Takeaways
- Regular and irregular hexagons have different area calculation methods.
- The apothem is crucial for determining hexagon area accurately.
- Hexagons have significant applications in nature, architecture, and design.
- Practical examples solidify understanding of hexagon area formulas.
- Comparing regular and irregular hexagon measurements enhances geometric comprehension.
FAQ
1. What is the difference between a regular and an irregular hexagon?
A regular hexagon has equal sides and angles, which means its area can be calculated easily using side length alone. An irregular hexagon, on the other hand, has sides and angles of varying lengths and measures, requiring more complex methods such as triangulation for **hexagon area calculation**.
2. How do I calculate the area of an irregular hexagon?
To calculate the area of an **irregular hexagon**, divide it into smaller, easily measurable shapes, like triangles or rectangles, and sum their areas. This triangulation approach allows for a comprehensive method to find **hexagonal area** accurately, utilizing multiple simple area formulas.
3. Can you explain how the hexagon area formula relates to its perimeter?
The hexagon’s perimeter is important in calculating area using the apothem method. The formulas demonstrate that the area can be influenced significantly by both the perimeter and the length of the apothem, which connects to the significance of **hexagon area in architecture** and design.
4. What are practical applications of hexagons in design?
Hexagons serve multiple purposes in design, from natural honeycomb structures to tiling and architectural plans. These shapes are favored for their ability to cover space efficiently while maintaining structural integrity. Their application is noteworthy in **hexagonal tiling** patterns seen frequently in flooring and wallpaper designs.
5. How can I visualize hexagon properties for better understanding?
Utilizing geometric visualization tools, such as drawing software or physical models, greatly aids in comprehending **hexagon geometry problems**. Such tools will showcase the relationships between side lengths, area, and perimeter more effectively, making learning interactive and engaging.
“`