Essential Guide to How to Calculate Producer Surplus: Understand Modern Economic Benefits in 2025
Essential Guide to How to Calculate Producer Surplus
Understanding Producer Surplus
Producer surplus is a critical concept in welfare economics that represents the difference between what producers are willing to accept for a good or service and the actual price they receive. This economic measure not only informs market efficiency but also highlights how producers benefit from market transactions. Essentially, producer surplus acts as an incentive for producers to supply goods, reflecting their willingness to produce at various prices. By understanding producer surplus, we can appreciate its role in influencing market dynamics and fostering economic growth.
Producer Surplus Definition and Implications
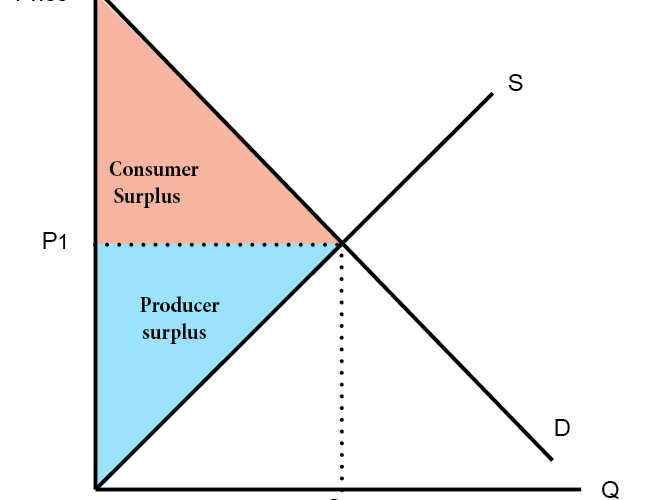
The producer surplus definition encompasses all the profits producers earn above the costs associated with production. This surplus is calculated by examining the area above the supply curve and below the market price level. For example, if a company produces goods at a cost of $50 but sells them for $80, the producer surplus is $30 per unit. The implications of this surplus extend to how producers adjust their production choices based on market signals and price settings. Consequently, a higher producer surplus may encourage greater output and investment in the sector. This flexibility demonstrates the interconnectedness of producer behavior and market conditions.
The Role of Market Prices in Producer Surplus
Market prices play a pivotal role in determining the level of producer surplus. As prices rise, the producer incentives often increase, driving more producers to enter the market or expand production. This phenomenon is directly related to the economic principle of supply and demand equilibrium, where prices gravitate towards a balance between supply and consumer demand. Changes in the market price, such as from economic growth or competition, can lead to significant changes in the surplus measurement. It’s essential for producers to analyze market conditions continuously so they can adapt their pricing strategies and production levels accordingly.
Measuring Producer Surplus: The Formula
To effectively understand how to calculate producer surplus, one must familiarize themselves with the producer surplus formula. The basic formula involves calculating the difference between market price and the minimum price that producers are willing to accept multiplied by the quantity sold. The formula appears as follows:
Producer Surplus = (Market Price – Minimum Acceptable Price) x Quantity Sold
For a more visual representation, producer surplus can also be illustrated through a producer surplus graph. Graphically, producer surplus is depicted as the area between the market price line and the supply curve, providing an intuitive understanding of surplus shifts caused by changes in supply or demand. By employing this method, stakeholders can assess the effect of market fluctuations on producers’ economic welfare and overall market efficiency.
Example of Producer Surplus Calculation
Let’s consider a practical example to illustrate the calculation of producer surplus. Assume a local farmer sells tomatoes at a market price of $5 per pound. However, the farmer’s cost of production, including labor and materials, amounts to $3 per pound, meaning the minimum price he would accept is $3. If the farmer sells 100 pounds of tomatoes, the calculation would be:
Producer Surplus = (5 – 3) x 100 = $200
This example demonstrates how understanding producer surplus can help farmers make informed decisions about pricing, production scale, and resource allocation. Effective evaluation of such data supports smarter business strategies for producers looking to maximize profits.
Surplus Calculation Methods
In addition to the basic formula, several other surplus calculation methods can provide deeper insights into market analysis. For instance, differential methods might be used to assess changes in producer surplus in response to market interventions, like price floors or ceilings. These methods consider the adjustment in supply and demand curves, offering to depict shifts resulting from government policies or existing market structures. Furthermore, comparative surplus analysis across different markets can unveil trends and impacts on producers under varying market conditions.
Benefits of Producer Surplus in Economic Context
The benefits of understanding producer surplus extend beyond mere calculations. In the grand scheme of economic theory, producer surplus signals extensive welfare benefits not only to producers but also to consumers. For instance, a thriving producer sector can create jobs and stabilize resources within a community, contributing to the overall economic productivity. This interconnectedness elevates the importance of analyzing how surpluses are generated and measured across different economic environments.
Impact on Consumers and the Economy
Analyzing the effect of producer surplus on consumer welfare reveals a multifaceted relationship. When producer surplus increases, it often results in lower prices for consumers as producers become more competitive in the marketplace. This dynamic manifests in enhanced overall economic welfare, as increased supply can lead to decreased prices, benefitting a larger consumer base. For example, when producers operate more efficiently, you may see a reduction in market prices, directly impacting how consumers perceive value and make purchasing decisions.
Market Efficiency and Resource Allocation
The relationship between producer surplus and market efficiency is crucial for understanding economic outcomes. Efficient markets effectively allocate resources, thus maximizing total economic surplus, which encompasses both producer and consumer surplus. The balance and optimization within market systems foster healthy competition where prices reflect the true value of goods and services offered. Furthermore, recognizing how resource allocation can influence profit maximization strategies prepares producers for fluctuations in demand and shifts in economic indicators.
Conclusion and Key Takeaways
In summary, understanding and calculating producer surplus is essential for stakeholders in any marketplace. This guide offers detailed insights into the definition, methods of calculation, and implications of producer surplus for economic growth and market stability. By employing comprehensive analysis, producers can make informed decisions that not only enhance their profitability but also contribute to market efficiency and consumer welfare.
Key Takeaways
- Producer surplus is crucial for understanding market incentives and economic behavior.
- Effective calculations of producer surplus help producers maximize profits and make informed production choices.
- The relationship between producer surplus and economic welfare underscores its significance beyond the immediate producer benefits.
- Market efficiency hinges on the optimal distribution of resources underscored by available surpluses.
- Producers need to continuously analyze market dynamics to adapt to changes in pricing and demand effectively.
FAQ
1. What does the term “producer surplus” mean?
Producer surplus refers to the difference between the amount producers are willing to accept for a good and the actual market price. It is crucial for understanding the profitability of producers and their incentives in the marketplace.
2. How can producer surplus impact market prices?
An increase in producer surplus often results in heightened competition among producers, which can lead to lower prices for consumers. This is beneficial as it expands consumer options while maintaining profitability for producers.
3. Why is understanding producer surplus important for welfare economics?
Understanding producer surplus is vital for welfare economics as it reflects the economic benefits producers receive, which impact overall market efficiency and consumer welfare. Effective surplus analysis can help understand how resources are allocated within an economy.
4. What methods exist to calculate producer surplus?
While the primary formula depends on the difference between price and minimum acceptable price, other methods include graphical analysis and differential methods, which can accommodate changes in supply curves and government interventions.
5. How does competition influence producer behavior?
In competitive markets, increased producer surplus motivates producers to optimize costs and improve production efficiency. This healthy competition drives innovation, allowing producers to better meet market demands while maximizing their welfare.